Introduction
Neuromas, schwannomas or so called neurilemoma are benign lesions that normally originate in the myelin sheath covering nerves.
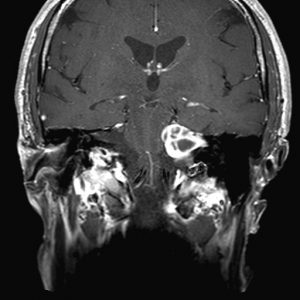
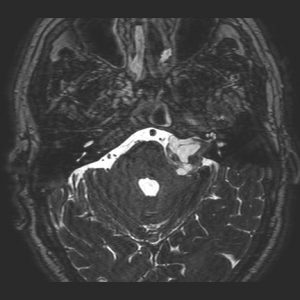
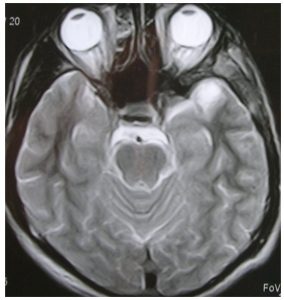
They may originate on any nerve but in the brain the most common site is the cerebellopontine angle. In this area the neuromas originated from the statoacoustic nerve or VIII cranial nerve and are called acoustic neurinomas.
Clinical signs
The statoacoustic nerve is responsible for hearing and balance and so the symptoms caused by growth of the neuroma in this area are hearing loss or deafness and balance disorders.
Should the lesion grow, it may cause headache, nausea, vomiting, affectation of the facial nerve controlling facial movement and the trigeminal nerve responsible for sensation in the face. Should it be large in size, it may cause compression of the brain stem and more important neurological disorders.
Diagnosis
In suspected diagnosis it is important to perform cranial magnetic resonance imaging of the cerebellopontine angle to make a good assessment of the lesion and the effect on surrounding structures.
Other tests may also be required: audiometry evoked hearing potentials, somatosensory evoked potentials (SEPs) to complete the diagnosis.