Parkinson’s disease (PD), also called idiopathic Parkinsonism or paralysis agitans, is a chronic neurodegenerative disorder that in time leads to progressive disability, produced as a result of the destruction, by as yet unknown causes, of pigmented neurons of the substantia nigra. Frequently classified as a movement disorder, Parkinson’s disease also unleashes disorders in cognitive functions, the expression of emotions and involuntary functions.
 This disease represents the second neurodegenerative disorder in frequency, behind Alzheimer’s disease. It extends all over the world and affects both men and women and usually appears after the sixth decade of life. However, apart from this tardive variety, there is another early version that appears in people under forty.
This disease represents the second neurodegenerative disorder in frequency, behind Alzheimer’s disease. It extends all over the world and affects both men and women and usually appears after the sixth decade of life. However, apart from this tardive variety, there is another early version that appears in people under forty.
At the present time, diagnosis is based on the clinical signs as no biological marker has been identified for this disease. For this reason, diagnosis is based on detection of the characteristic triad rigidity-tremor-bradykinesia and the absence of atypical symptoms, although the exclusion of other possible disorders using brain imaging techniques or blood analyses is also important.
Surgery for Parkinson’s disease
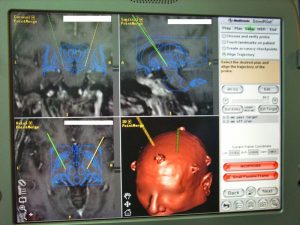
The surgical treatment of Parkinson’s disease has been an option since the 80’s. The technique currently used is deep brain stimulation (DBS) of a very specific area of the brain, the most common being the Subthalamic nucleus.
Not all patients with Parkinson’s disease are good candidates for surgery. Surgical treatment is indicated when the motor symptoms (tremors, dyskinesias, gait disorders, stiffness, bradykinesia) do not respond sufficiently to pharmacological treatment.
Deep brain stimulation (DBS) is a surgical treatment that can reduce some of the symptoms associated with Parkinson’s disease. It is an adjustable therapy, and if necessary, reversible. It uses a device that stimulates the brain electrically, blocking the signals that cause incapacitating motor symptoms.
It consists of two brain electrodes connected to a stimulus generator (battery) similar to a heart pacemaker. The battery is usually placed in the subcutaneous tissue of the abdomen or beneath the clavicle, wherever the patient prefers.
The parameters stimulation generator can be adjusted by a remote device to the precise needs of the patient.
The risks/side effects of deep brain stimulation therapy are very infrequent, and may include risks related to the surgery itself, complications with the device or the stimulation. The risks related to the stimulation can be resolved by adjusting the stimulation parameters.



