The phakomatosis refers to a group of neurocutaneous disorders of multifactorial aetiology and genetic base. In general these disorders favour the appearance of neurological and skin tumours.
Different types of phakomatosis: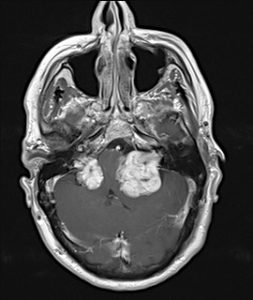
- Neurofibromatosis Type I: characterised by the appearance of a “whitish” skin spot, affectation of the central nervous system (optic nerve gliomas are typical), appearance of neurofibromas and Lisch nodules.
- Neurofibromatosis Type II: also called central neurofibromatosis as tumours are predominant in the central nervous system: bilateral acoustic neuromas, meningiomas, gliomas, etc.
- Sturge-Weber Syndrome: associated with angiomas in different locations, cerebral calcification causing epileptic seizure, neurological disorders (learning problems, etc.) and glaucoma.
- Von Hippel-Lindau Syndrome: causing anomalous growth of retina and cerebellar vessels and a susceptibility to kidney tumours.
- Tuberous sclerosis: produce the formation of tumours in the central nervous system, retina, skin, lungs, kidneys and heart.
Treatment
As shown in the introduction this group of disorders cause susceptibility to different tumours throughout life. Experience in these disorders is essential for diagnostic management of the disease and determine the most suitable moment for taking any surgical action.



