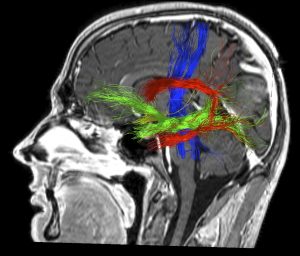
 The term neuronavigation was coined in the 80’s. This technique was designed to enable reaching deep regions of the brain producing the least possible damage to the brain tissue surrounding the area. Authors such as Yasargil proposed reaching these regions by dissecting brain sulci. The term was later adopted by the workstations that enable locating a determined area on the basis of references previously entered into the computer equipment.
The term neuronavigation was coined in the 80’s. This technique was designed to enable reaching deep regions of the brain producing the least possible damage to the brain tissue surrounding the area. Authors such as Yasargil proposed reaching these regions by dissecting brain sulci. The term was later adopted by the workstations that enable locating a determined area on the basis of references previously entered into the computer equipment.
Technique:
Until recently, the use of this technique required pre-operative CT or MRIimages, but the introduction of intraoperatory CT and MRI enable omitting this step in Centers where the technology is available. The system locates different anatomical points and superimposes these points on those from the imaging tests enabling surgeons to know their precise location by simply entering a point into the system. It is a bit like putting on a made-to-measure mask and after removing the mask giving points inside the mask to the machine which then tells us the equivalent point inside our skull.
Advantages:
It is especially useful in the location of cerebral cortex lesions as it permits optimum centring of the craniotomy. It is also useful for the location of deep brain lesions as it enables studying the approach before performing the surgery. The greatest advances with these units is that they are more and more precise, and so procedures that required the placement of stereotaxic frames, deep brain biopsies, functional surgery, etc., and now be performed with new neuronavigation units, thus making the whole procedure more comfortable.
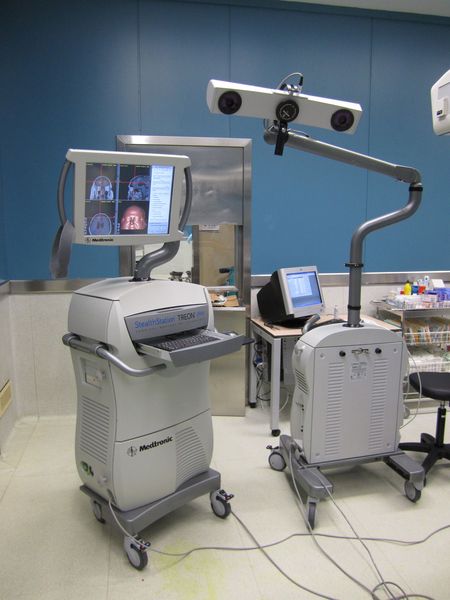


 The term neuronavigation was coined in the 80’s. This technique was designed to enable reaching deep regions of the brain producing the least possible damage to the brain tissue surrounding the area. Authors such as Yasargil proposed reaching these regions by dissecting brain sulci. The term was later adopted by the workstations that enable locating a determined area on the basis of references previously entered into the computer equipment.
The term neuronavigation was coined in the 80’s. This technique was designed to enable reaching deep regions of the brain producing the least possible damage to the brain tissue surrounding the area. Authors such as Yasargil proposed reaching these regions by dissecting brain sulci. The term was later adopted by the workstations that enable locating a determined area on the basis of references previously entered into the computer equipment.
